ecosystem-guides.com
....exploring the planet's ecosystems
NEOTROPICAL
(Amazonian) Lowland Tropical Rainforest
The rainforest of the Neotropics covers a huge geographical area, from southern Brazil north to southern Mexico. Within that area, it also varies in form and species composition as it grows from sea-level in the lowlands of the Amazon, along the coast of Brazil, to the cloud forest in the Andes, and the seasonally dry forest of Central America and the Caribbean islands. But the largest and most famous of these rainforest habitats is the lowland tropical rainforest centred on the Amazon basin.
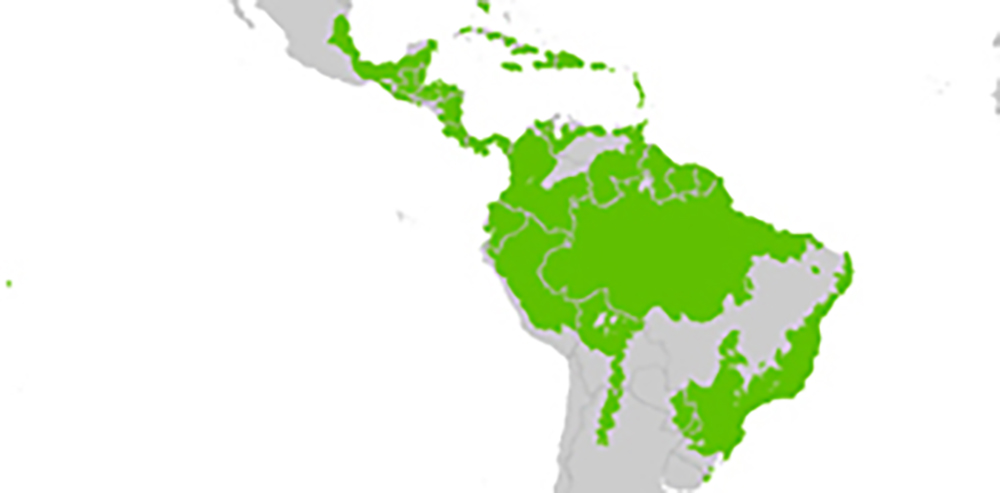 Map of Neotropical Moist Forest (Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=1550301)
Map of Neotropical Moist Forest (Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=1550301)Much of the rainforest in the lowlands of the Amazon is seasonally flooded. After heavy rain the overflow of water from the main rivers and tributaries creates several hundred thousand square kilometres of 'flooded forest'. These flooded forests represent between 3-4% of the Amazon basin. The water may rise up to 15 metres, and flow 20 kilometres in from the main rivers.
They are generally categorized into the Varzea and the Igapo. The former is created by the muddy waters of main white water rivers, the latter by the clearer 'black water'. The Varzea flooding comes and goes quickly, while the Igapo forest may remain flooded for half of the year. The former are nutrient rich waters, flowing from the Andes, and thus have higher productivity. The white water flooded Varzea also have higher diversity of species, while the black water Igapo floodplains are less diverse, dominated by a few species of Legume. On this website, these flooded forests overlap with the more open Neotropical freshwater wetlands.
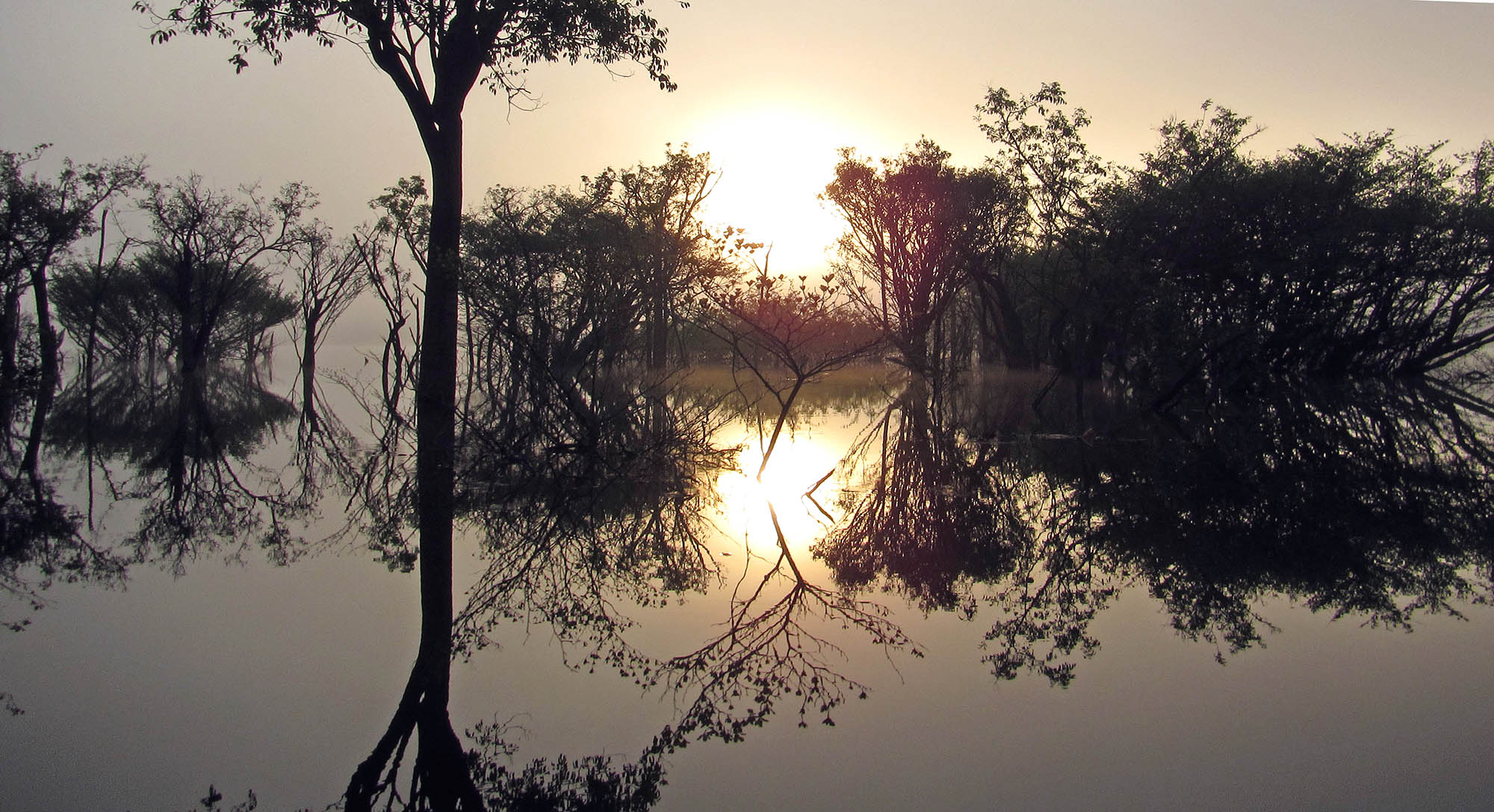 the seasonally flooded forests of the Amazon
the seasonally flooded forests of the AmazonAs with most tropical rainforests around the world (except south-east Asia), there are no species that dominate the rainforest canopy. Instead, there is a high diversity but low abundance of specific species. One of the notable families is the Malvaceae, which includes:
 Ceiba pentandra 'Kapok' (Ecuador).
Ceiba pentandra 'Kapok' (Ecuador). Apeiba sp, 'Monkeys Comb', (Yarina Lodge, Ecuador).
Apeiba sp, 'Monkeys Comb', (Yarina Lodge, Ecuador).Another family of smaller shrubs is the Verbanaceae, which includes the ubiquitous 'Snake Weed'.
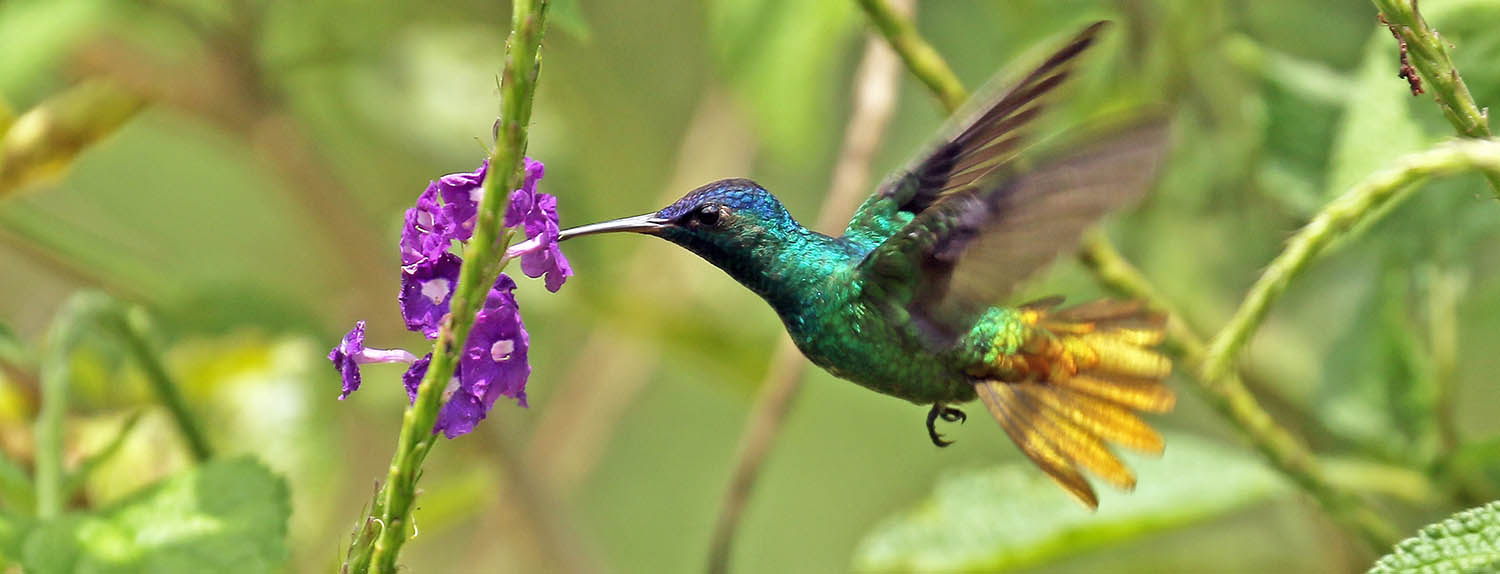 Stachytarpheta are popular with butterflies and hummingbirds (Amazonia Lodge, Peru).
Stachytarpheta are popular with butterflies and hummingbirds (Amazonia Lodge, Peru).The rainforests of the tropical Americas have the highest diversity of insects in the world. It has been reported that you will find more species of ants on a single tree in a Neotropical rainforest than occur across the entire country of England.
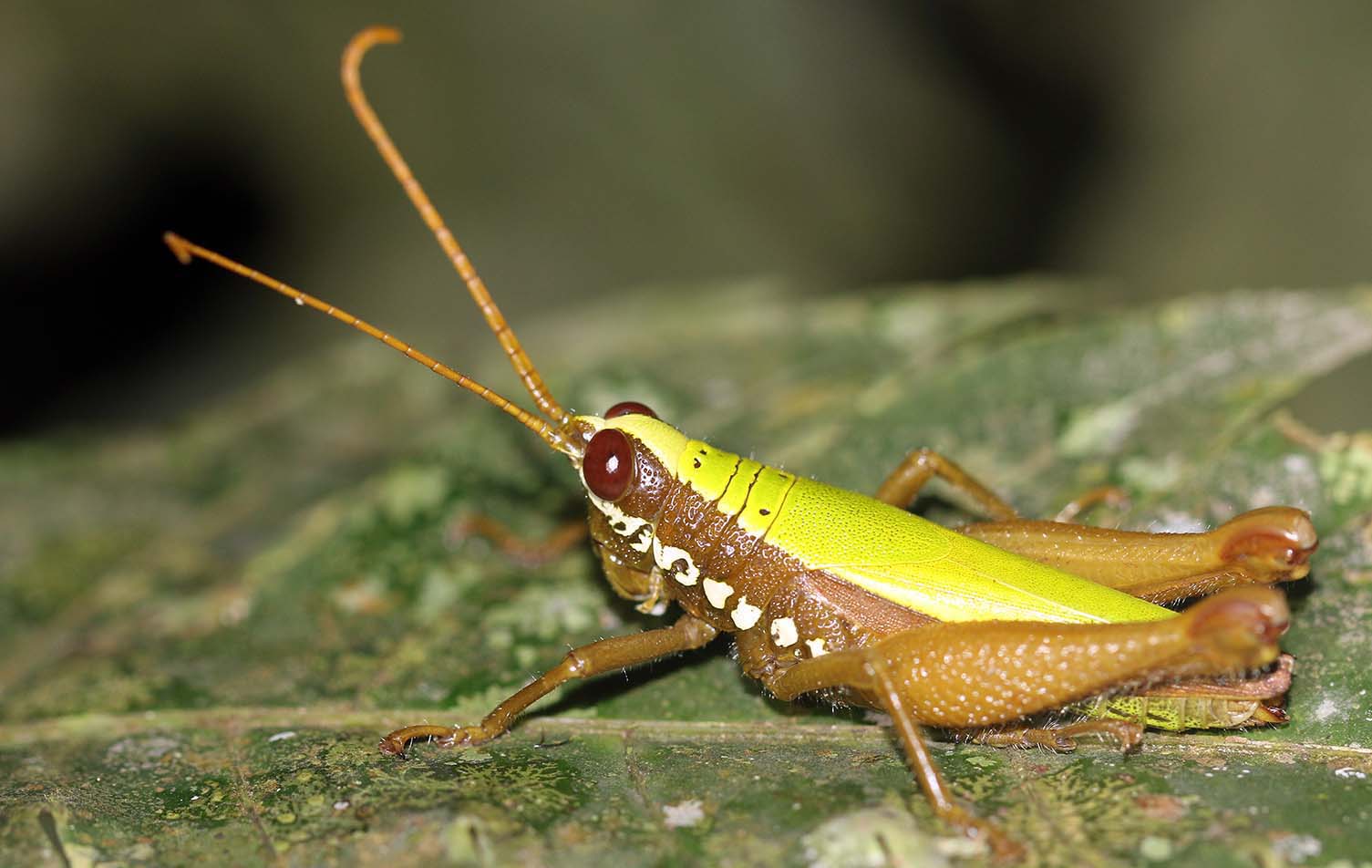

The insects of this order Orthoptera include the Crickets & Katydids, and Grasshoppers. Generally, the nocturnal crickets are duller coloured, while the diurnal grasshoppers can be brighter colours; however, in the tropical rainforest crickets are often colourful bright greens. Their loud calls give away their presence.
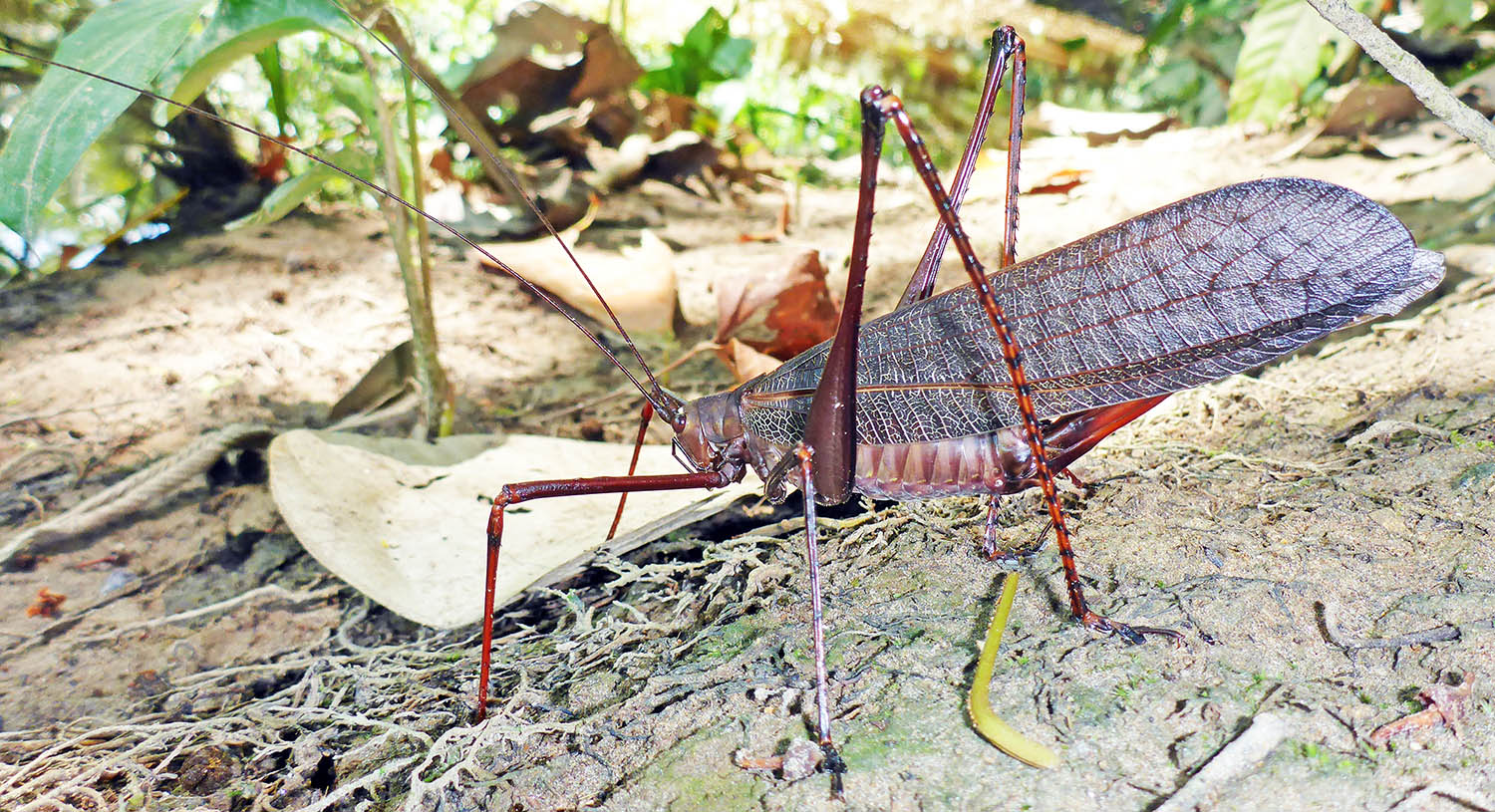 The huge 'Red-winged Grasshoppers' (Yarina Lodge, Ecuadorian Amazon).
The huge 'Red-winged Grasshoppers' (Yarina Lodge, Ecuadorian Amazon).One of the more interesting groups are the 25 or so species of Hamadryas 'Cracker Butterflies'. They are usually spotted, and sometimes blend in when seen perched on trunks upside down. They get their common name from make a crackling sound during territorial displays. Unlike most other butterflies they don't feed on nectar from flowers, but are attracted to rotting fruit on the forest floor, sap and even animal dung.
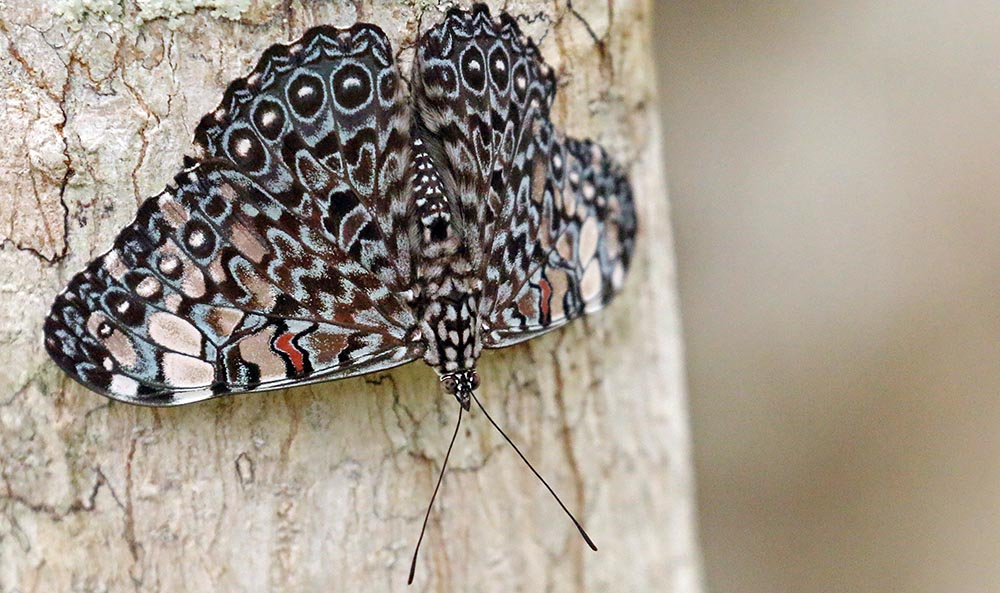 'Cracker Butterfly' (Villa Carmen Lodge, Peru).
'Cracker Butterfly' (Villa Carmen Lodge, Peru).Within the order Hymenoptera is the family Formicidae, which contains over 1000 species of ants in the Amazon region alone.
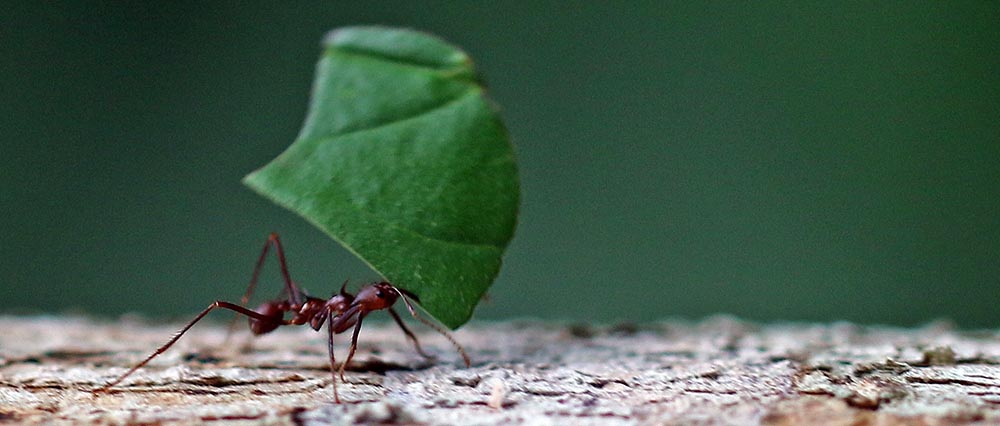
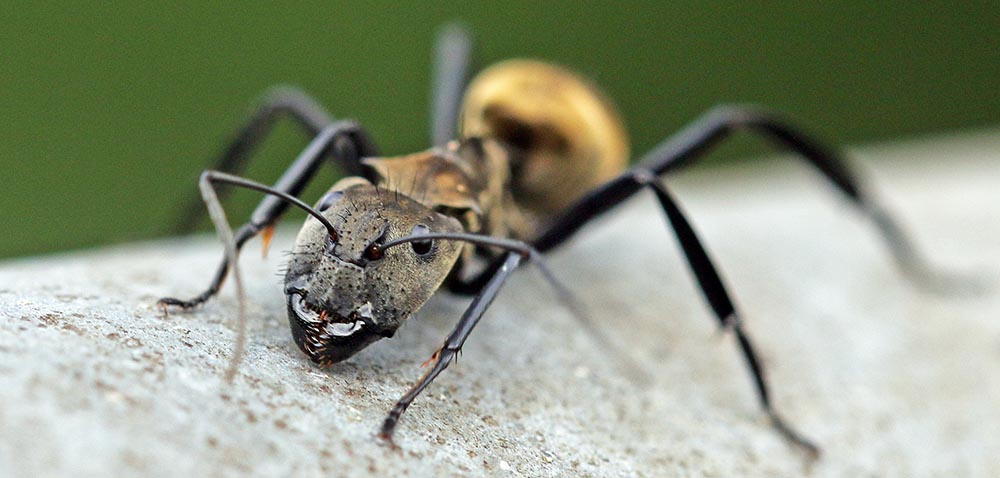 'Golden Carpenter Ant', (canopy tower, Amazonia Lodge, Peru).
'Golden Carpenter Ant', (canopy tower, Amazonia Lodge, Peru).If you see a line of leaves walking up a tree, you are witnessing 'Leaf-cutter Ants' at work.

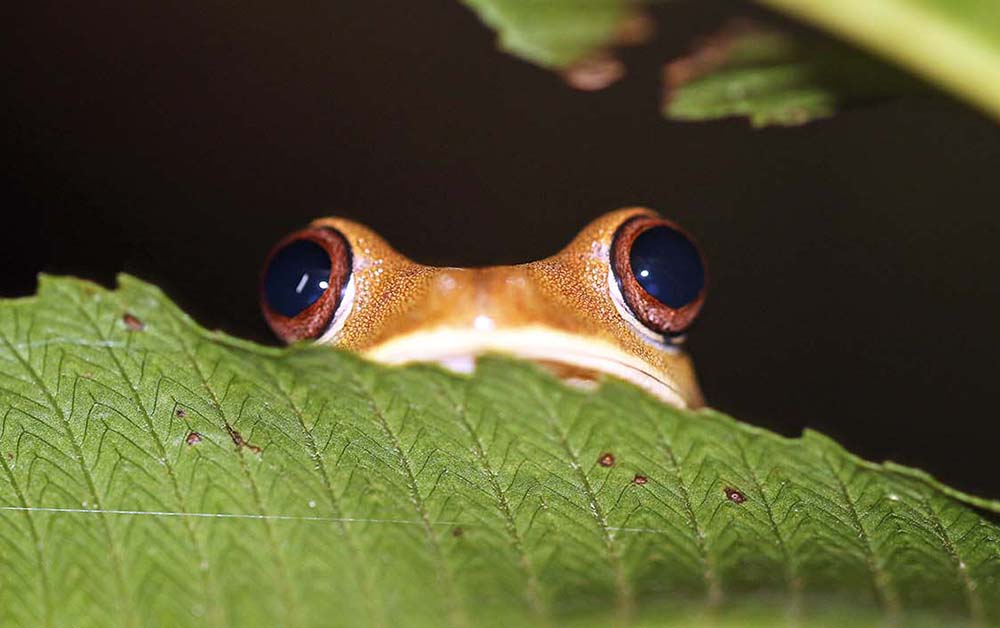
Frogs are amphibians without tails. And with those big eyes and floppy limbs and no teeth, they are pretty cute!

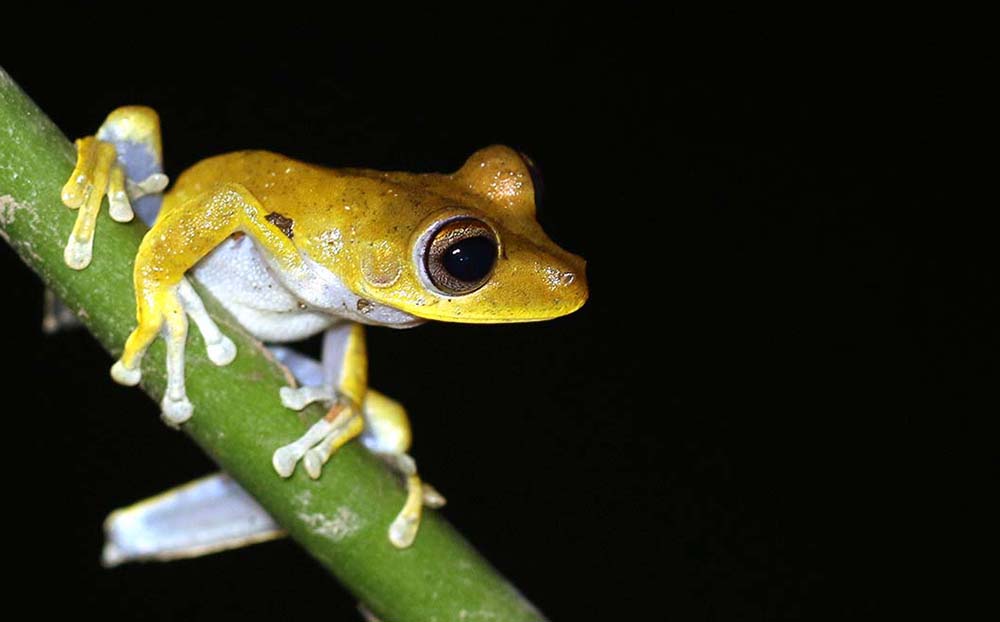
The family Hylidae incudes the classic tree frogs. As the name suggests, they are often found calling or climbing on branches in trees or bushes. Much of their morphology reflects this lifestyle; they are often green in colour, with long limbs for jumping, and large bulging eyes for judging distances. It is a large and widespread family across the tropics and warmer parts of the world, and they are split into several different sub-families that are sometimes treated at their own families, such as the Boana.
 Boana spp. 'Gladiator Tree Frogs'
Boana spp. 'Gladiator Tree Frogs'The (sub) family Phyllomedusidae includes the 'Leaf Frogs' and Phyllomedusa, the 'Monkey Frogs'.
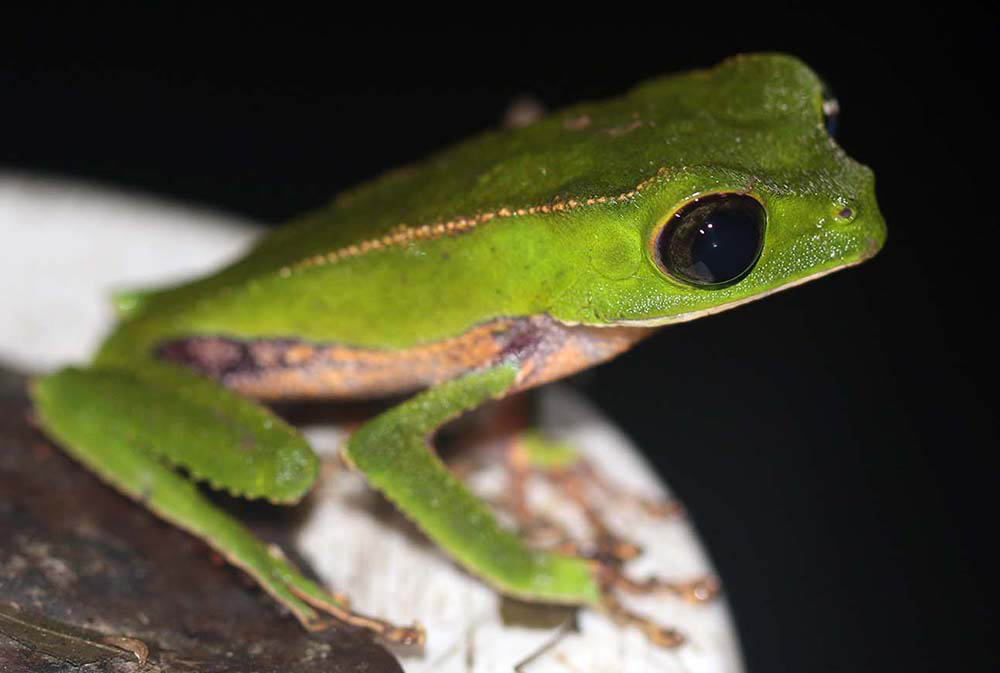

The most familiar amphibian family to most pople, and the most widespread, is the family Bufonidae, the '(True) Toads'
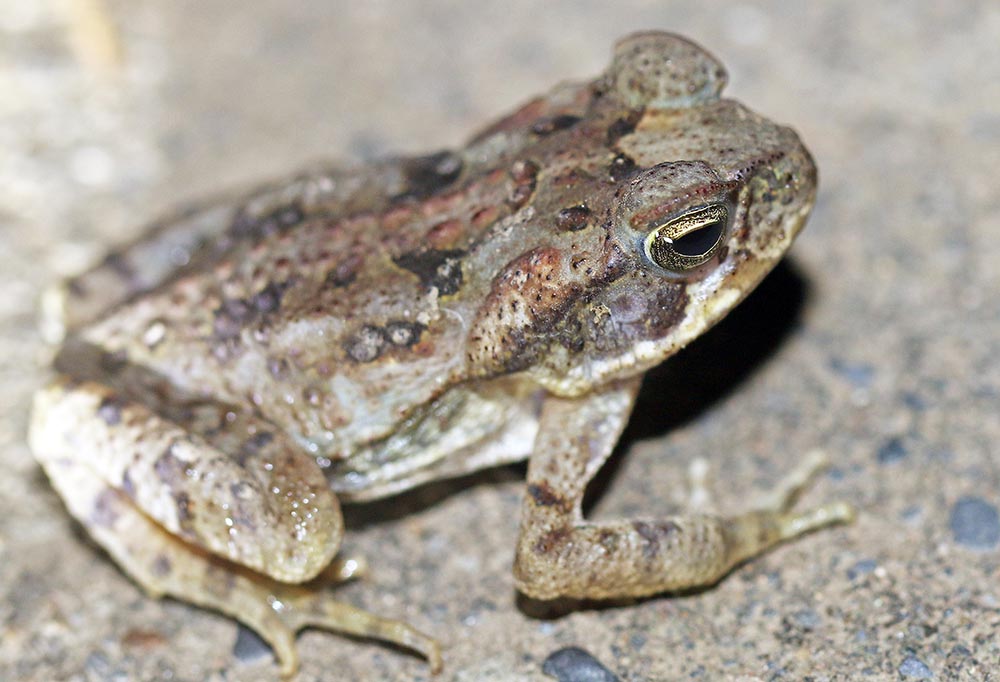 Rhinella marina 'Giant Neotropical Toad', 'Marine Toad'.
Rhinella marina 'Giant Neotropical Toad', 'Marine Toad'.The most famous amphibians within the Neotropical rainforest is no doubt those in the family Dendrobatidae: the 'Poison Arrow/Dart Frogs'. These frogs are usually small but stand out from the rainforest floor as they are often colourful. The poison arrow frogs are, as the common name suggests, toxic to eat. Thus, they walk around th forest floor in the daytime and in the open and not worried about being molested; unless a big human like me comes along. They are found in rainforests & associated habitats, only in South & Central America (although there is a sinmila looking group of frogs in Madagascar).
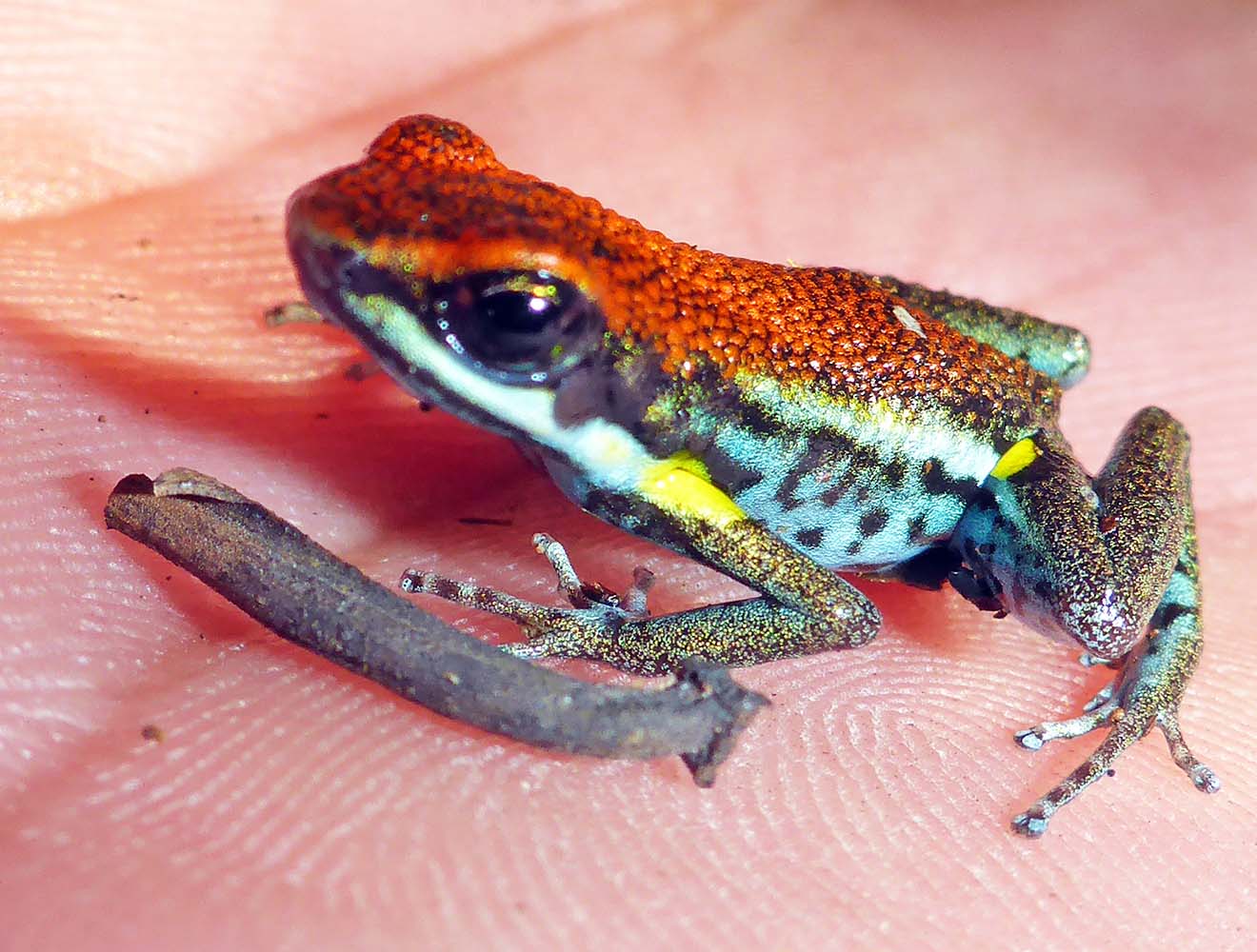 Ameerega bilinguis, 'Ecuador Poison Frog'.
Ameerega bilinguis, 'Ecuador Poison Frog'.The Iguanids are the most obvious group of lizards in the Neotropical forests. One group of Iguanids are the Neoptropical Ground Lizards of the family Tropiduridae.
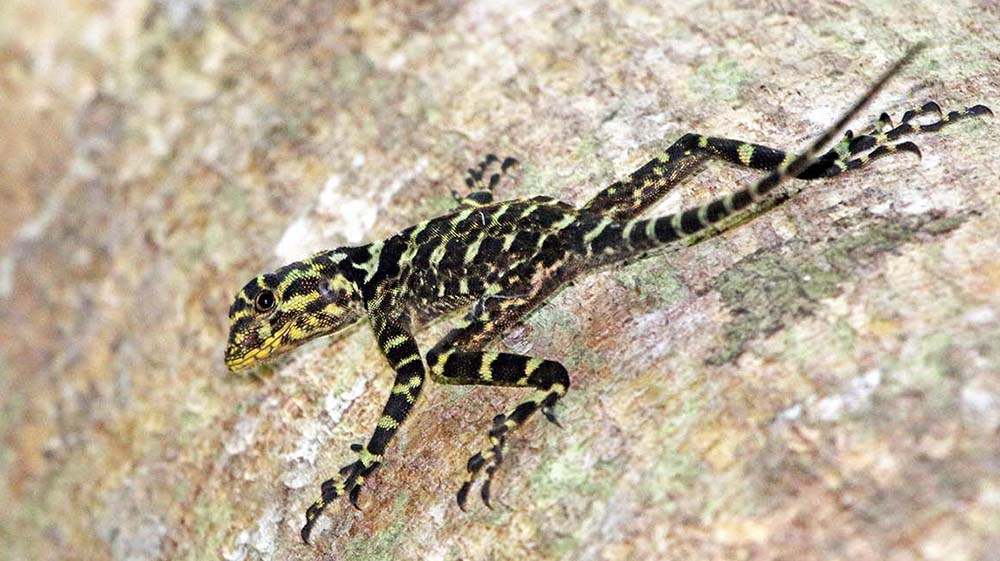 'Racerunner Lizard'.
'Racerunner Lizard'.There are some large snakes in the Neotropical forests, such as the Boa Constrictors. Depending on taxonomy, there are five species. They are a lie-and-wait predator and strike and coil around their prey, cutting off blood circulation to their victim, then swallowing. They are found across the tropical parts of Central and South America.
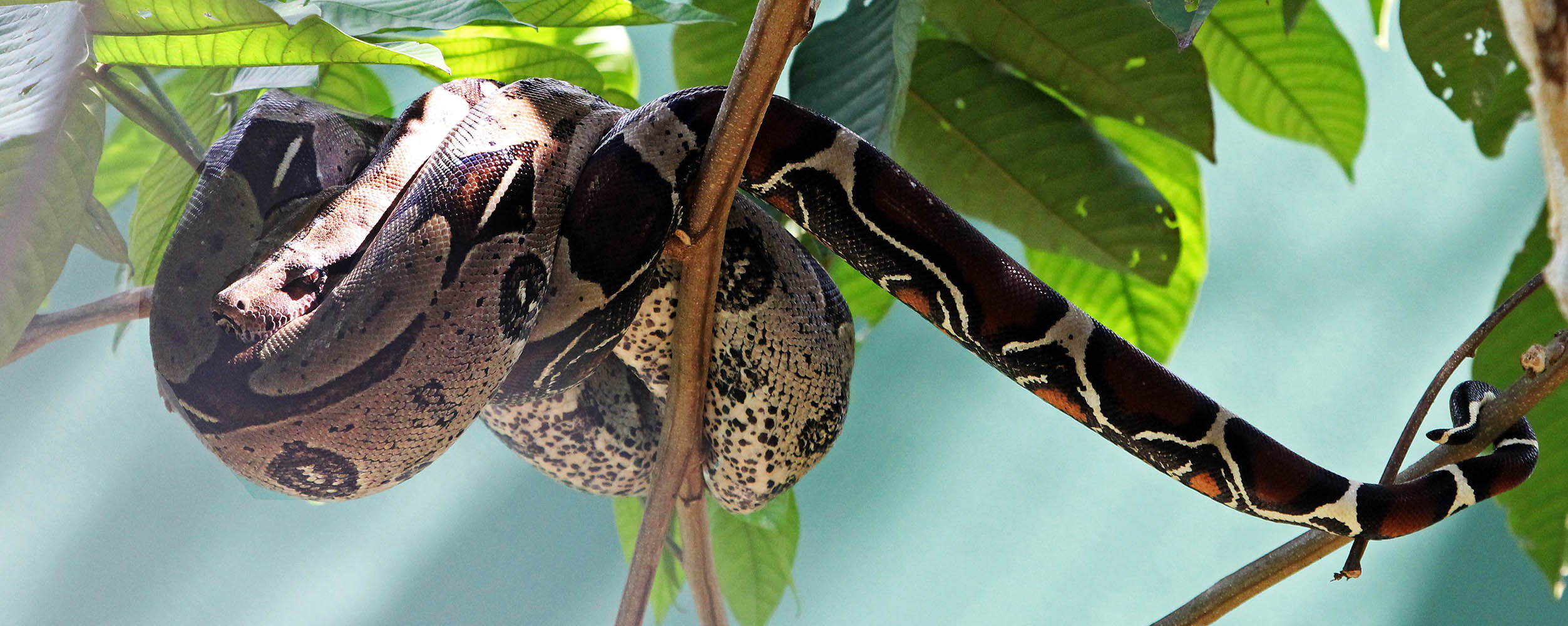 'Boa Constrictor'.
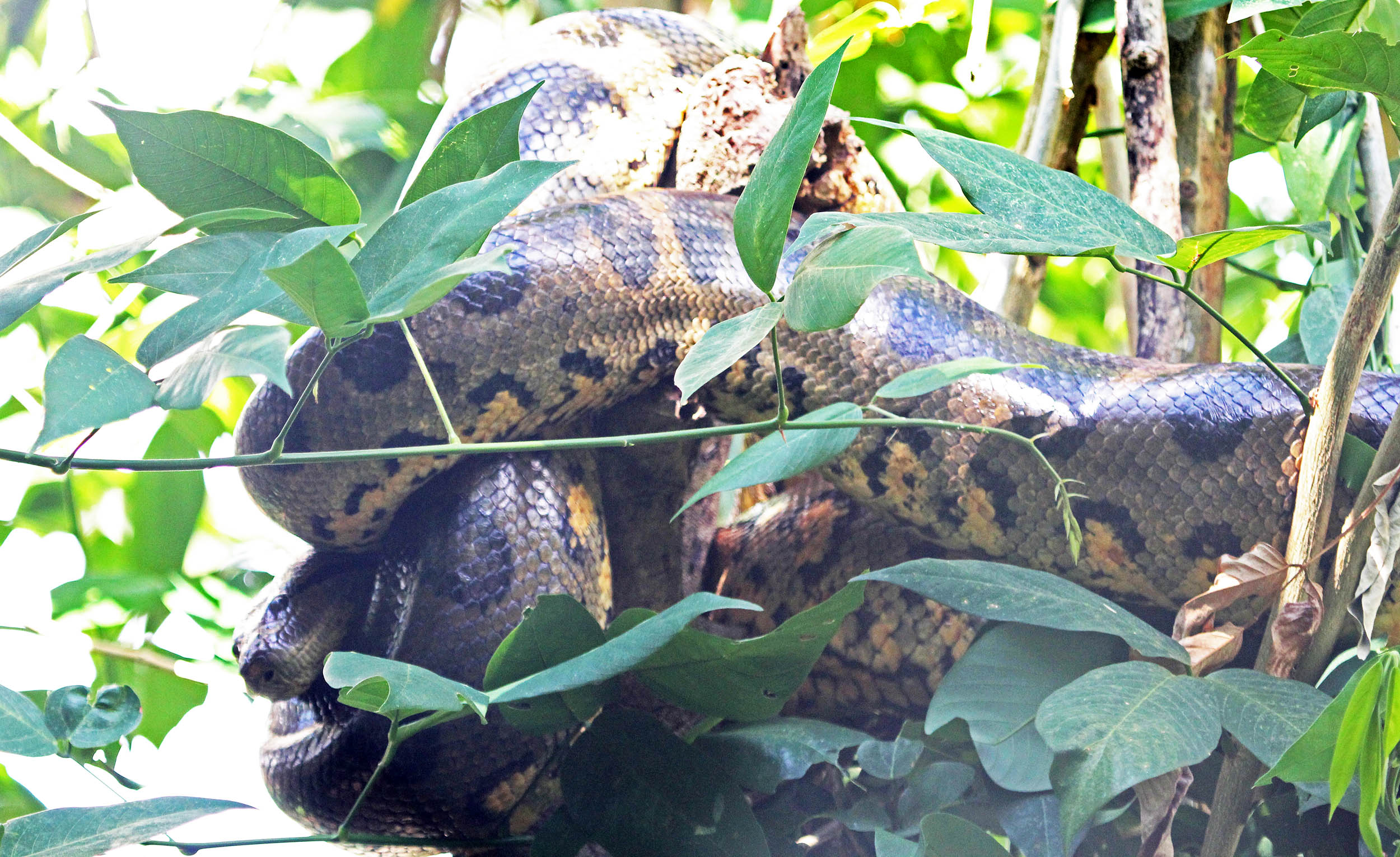
'Boa Constrictor'.However, the biggest snakes in the Neotropical forests are the infamous Anacondas.

Many of the smaller more commonly seen snakes belong to the family Colubidae.
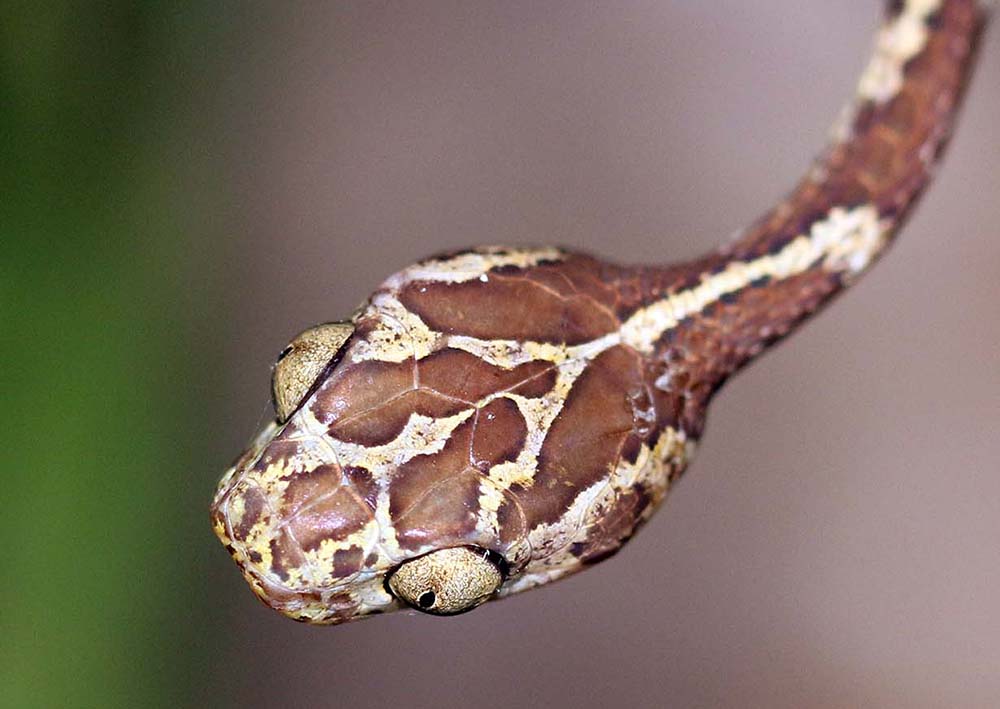 'Blunthead Tree Snake', (Yarina Lodge, Ecuador)
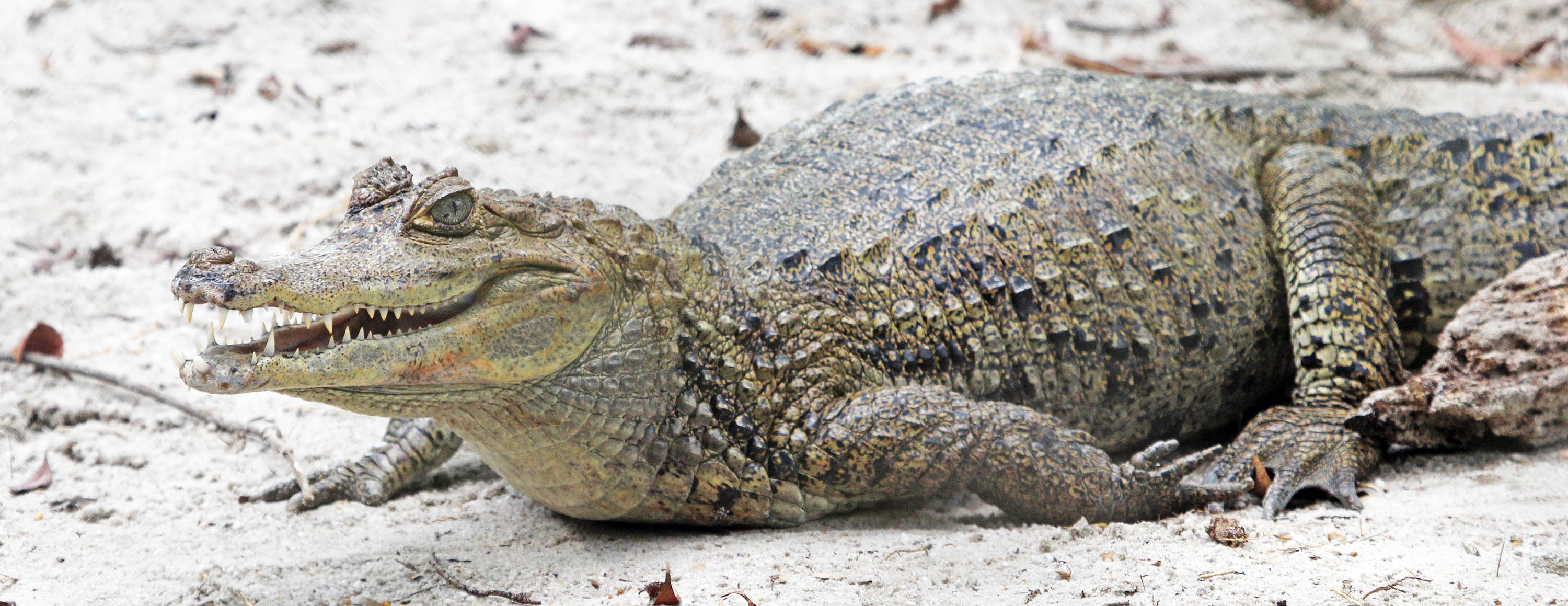
'Blunthead Tree Snake', (Yarina Lodge, Ecuador)The largest reptiles are the crocodilians. 'Black Caiman'. Growing up to 5 metres; thus it is considered to be the apex predator in lowland Amazonian rainforest.

Members of the family Cracidae (including Guans, Curassows, and Chachalaca) are often seen on the floor of the rainforest or perched on lower tree limbs on the edge.
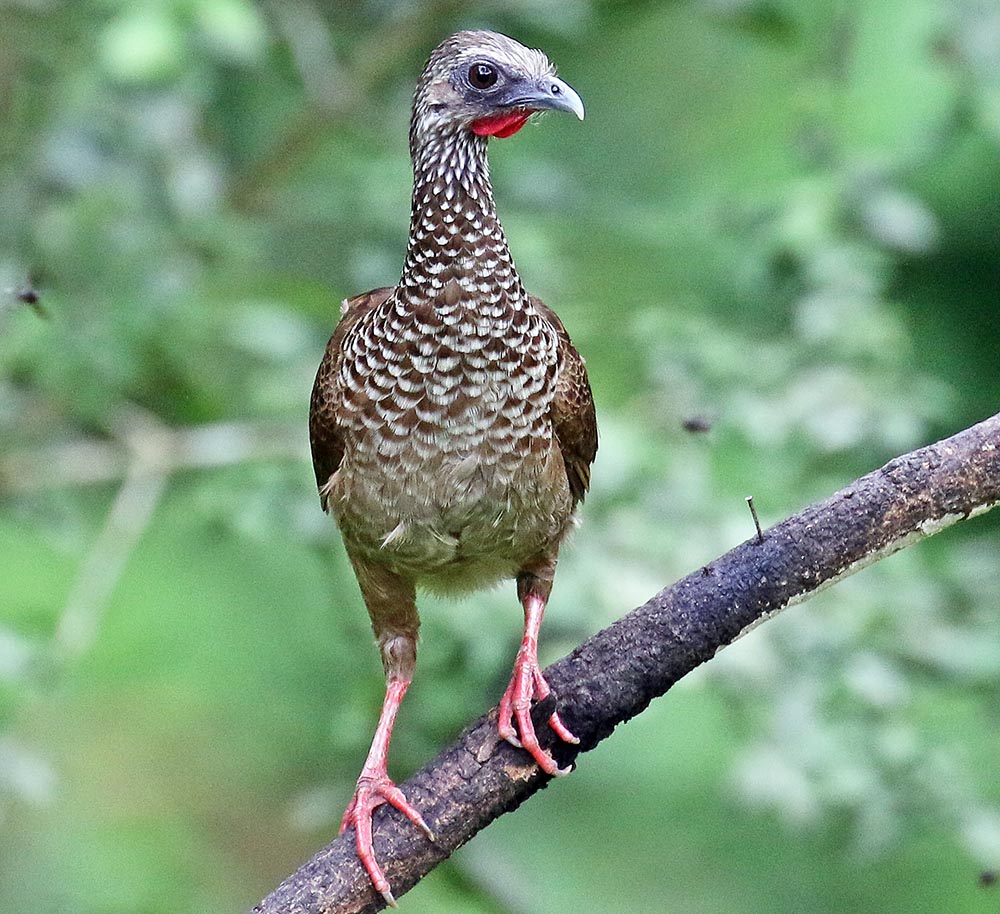 Speckled Chachalaca', (Amazonia Lodge, Peru).
Speckled Chachalaca', (Amazonia Lodge, Peru).There are over 350 species in the large Hummingbird family Trochilidae. They are known as 'hummingbirds' because of the relatively loud humming sound from the beating of their wings. When I first heard it, I thought it was a growl from a predatory mammal! The smaller species can flap their wings up to 80 times a second.
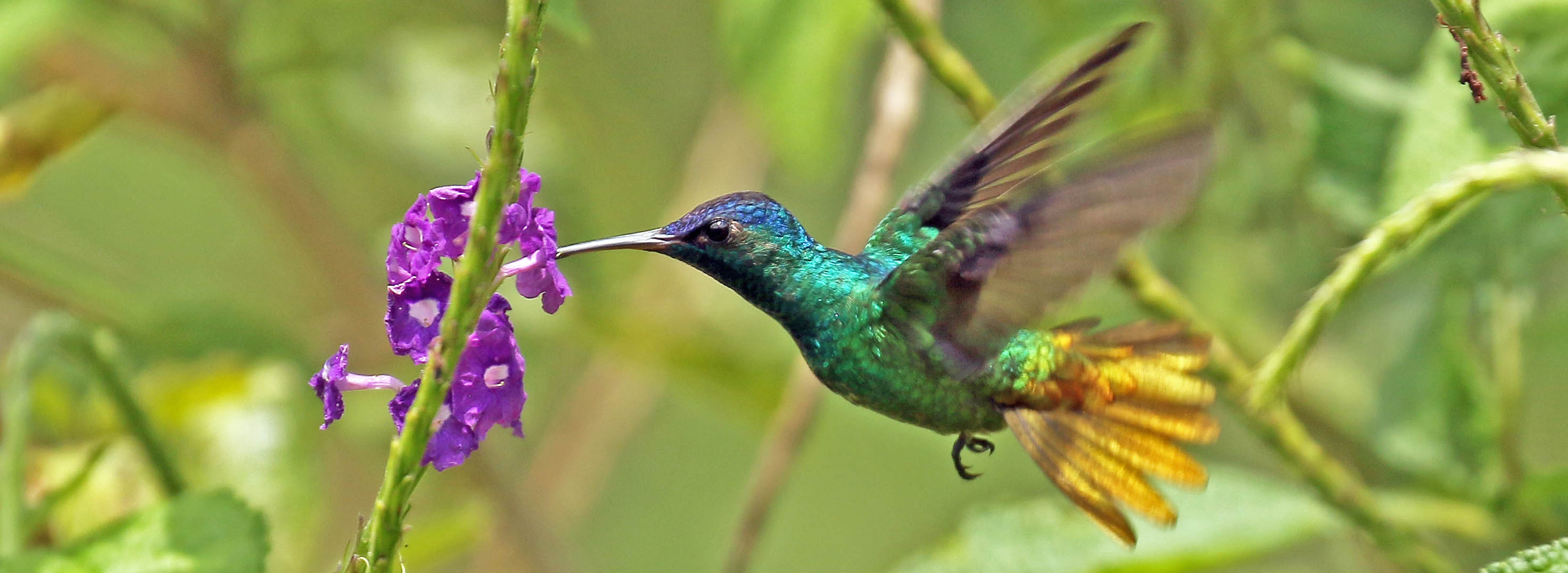 'Golden-tailed Saphire' (Amazonia Lodge, Peru).
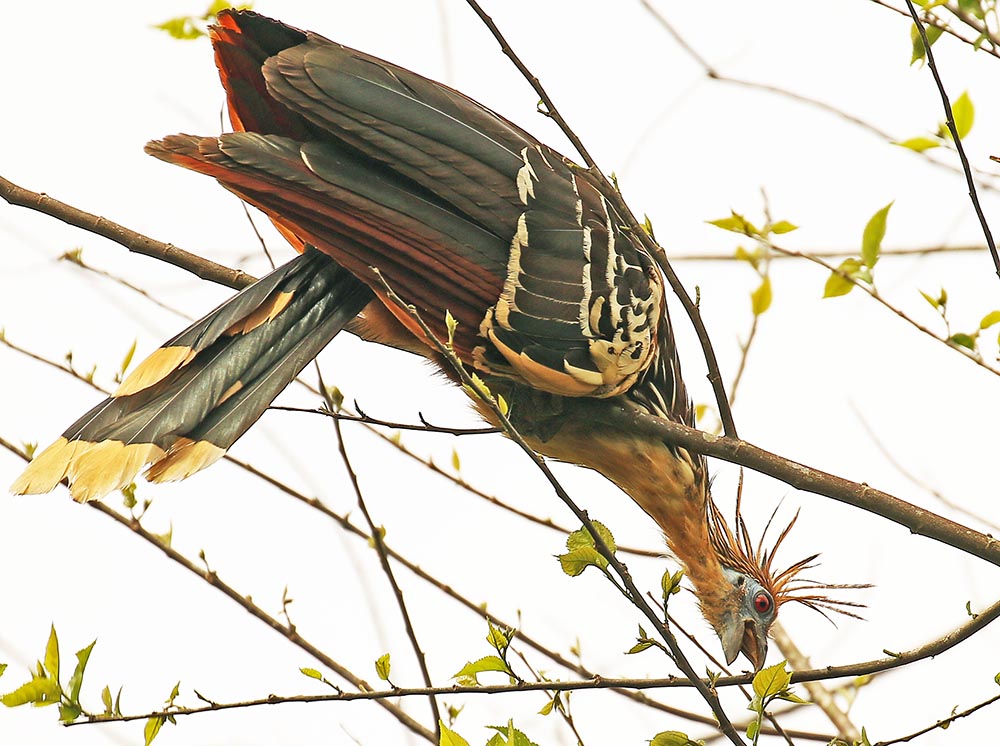
'Golden-tailed Saphire' (Amazonia Lodge, Peru).The monotypic family Opisthocomidae includes just one species, the famous 'Hoatzin', a large bird with a blue face and messy crest that climbs about noisily in waterside trees clumsily, often stretching and grunting. Unlike most other birds, it is mostly a folivore. It is only found in swampy habitats in South America.

The Neotropical forests (and other more open habitats of the Americas) include large scavengers known as 'New World Vultures'.
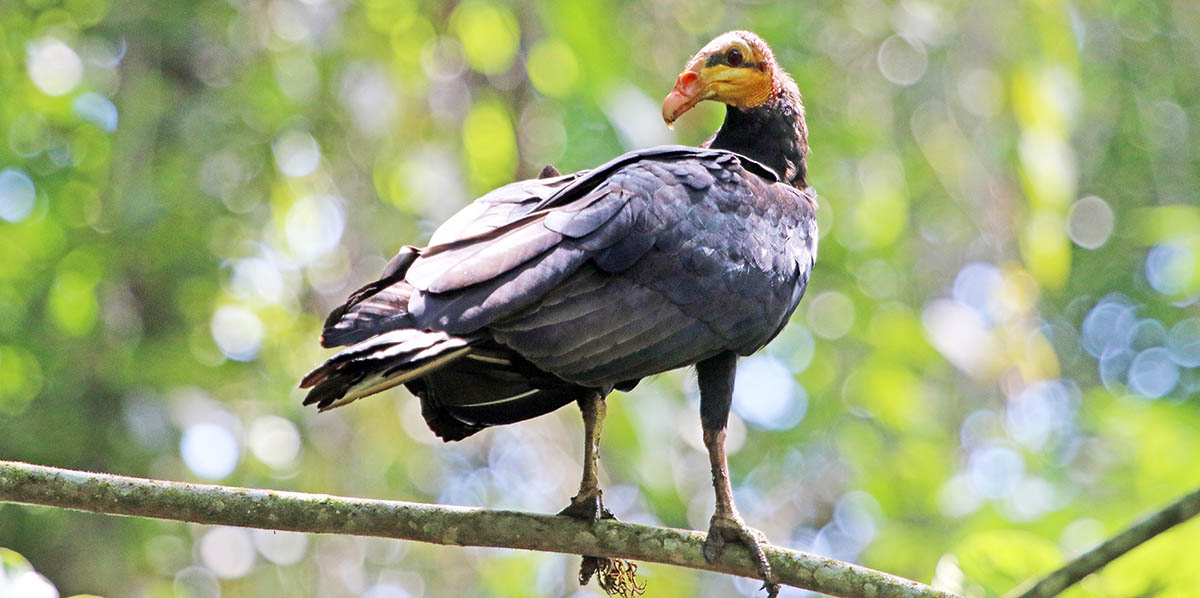 'Greater Yellow-headed Vulture', (Yarina, Amazon, Ecuador).
'Greater Yellow-headed Vulture', (Yarina, Amazon, Ecuador).There are many groups of colourful and strange Neotropical rainforest birds...
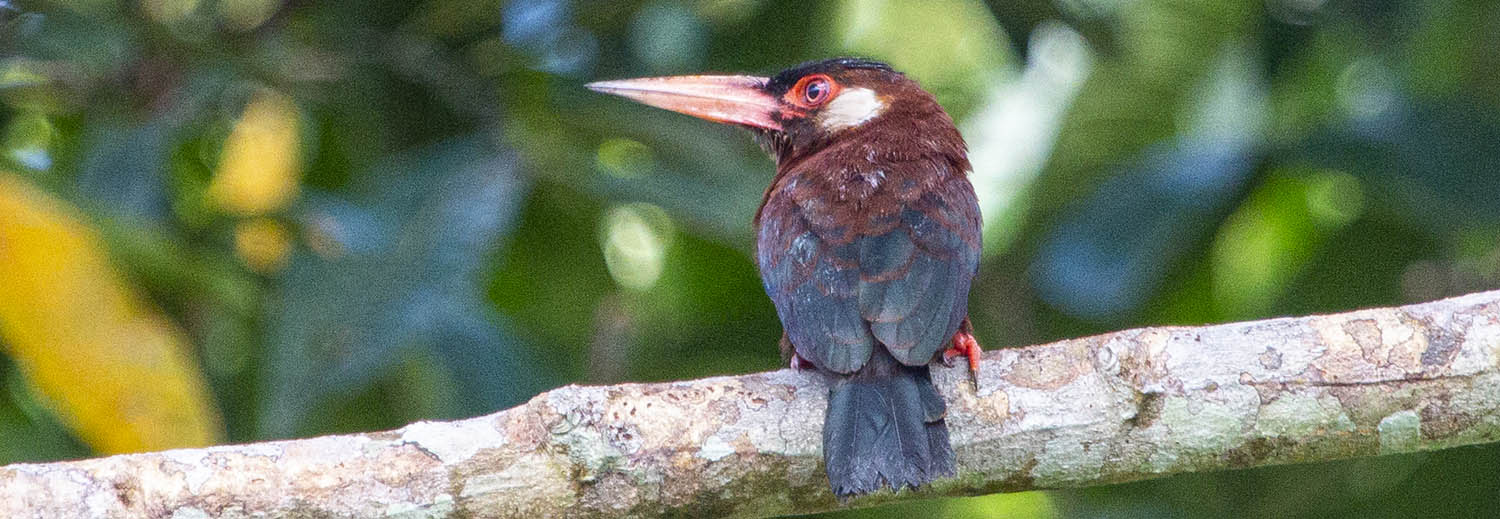 'White-eared Jacamar', (Yarina, Amazon, Ecuador).
'White-eared Jacamar', (Yarina, Amazon, Ecuador).Some of the more loud and obvious birds are in the 'New World Blackbirds' the Family Icteridae, such as the Oropendolas.
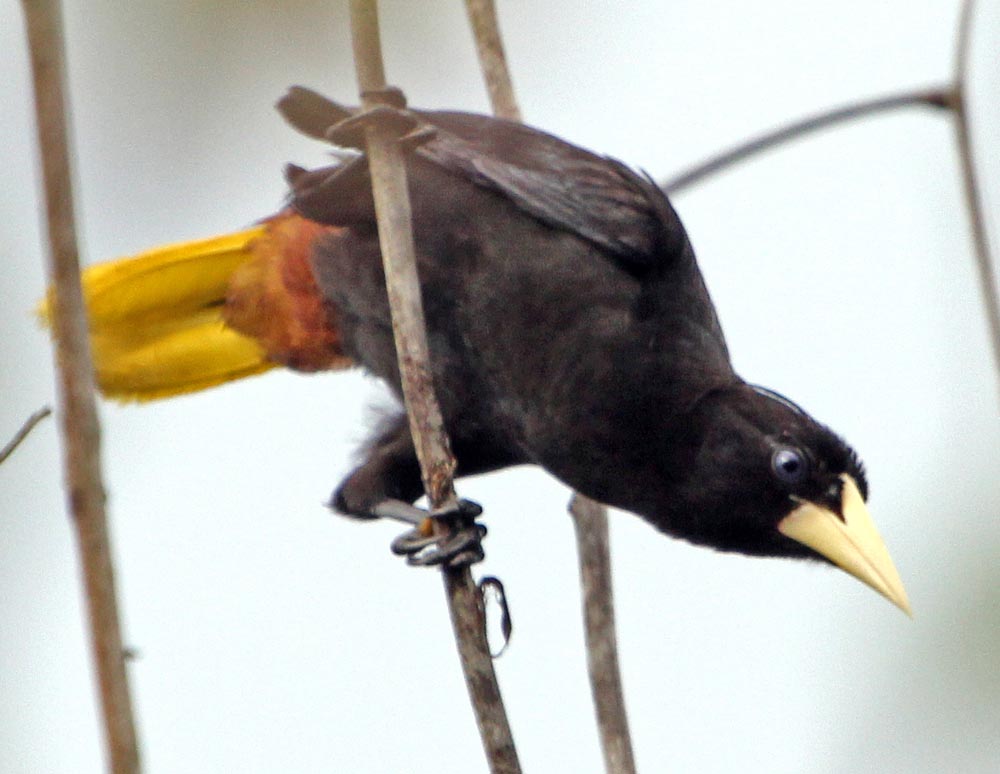 'Crested Oropendola'.
'Crested Oropendola'.Tanagers are one of the most colourful and diverse group of birds in the Neotropical jungle. They are the second largest family of birds, with over 200 species. Many are colourful, and most are distinct enough to be easily recognisable. All the species in the Tanager are restricted to the Neotropics; many have small distributions.
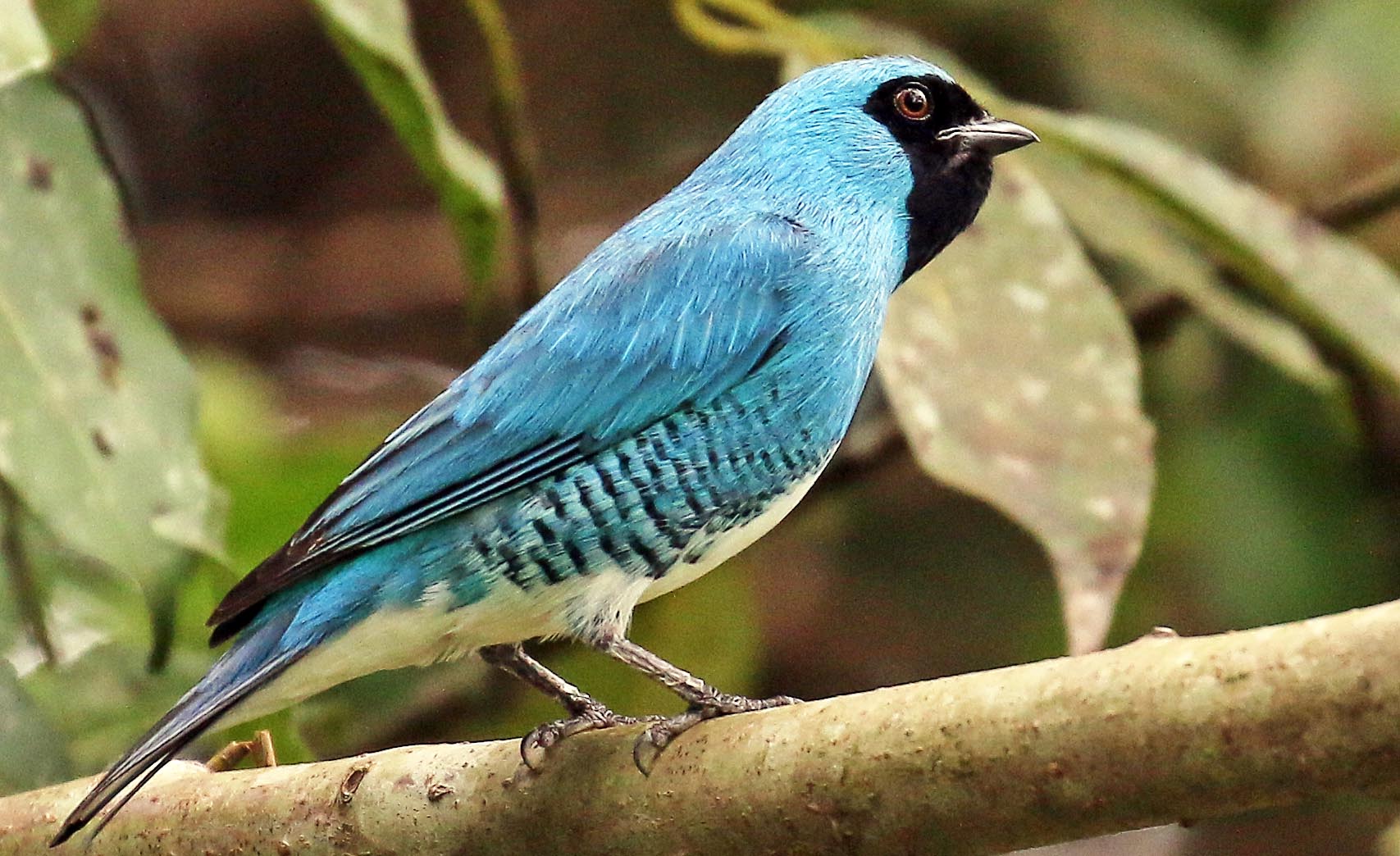 Swallow Tanager', (Villa Carmen, Peru).
Swallow Tanager', (Villa Carmen, Peru).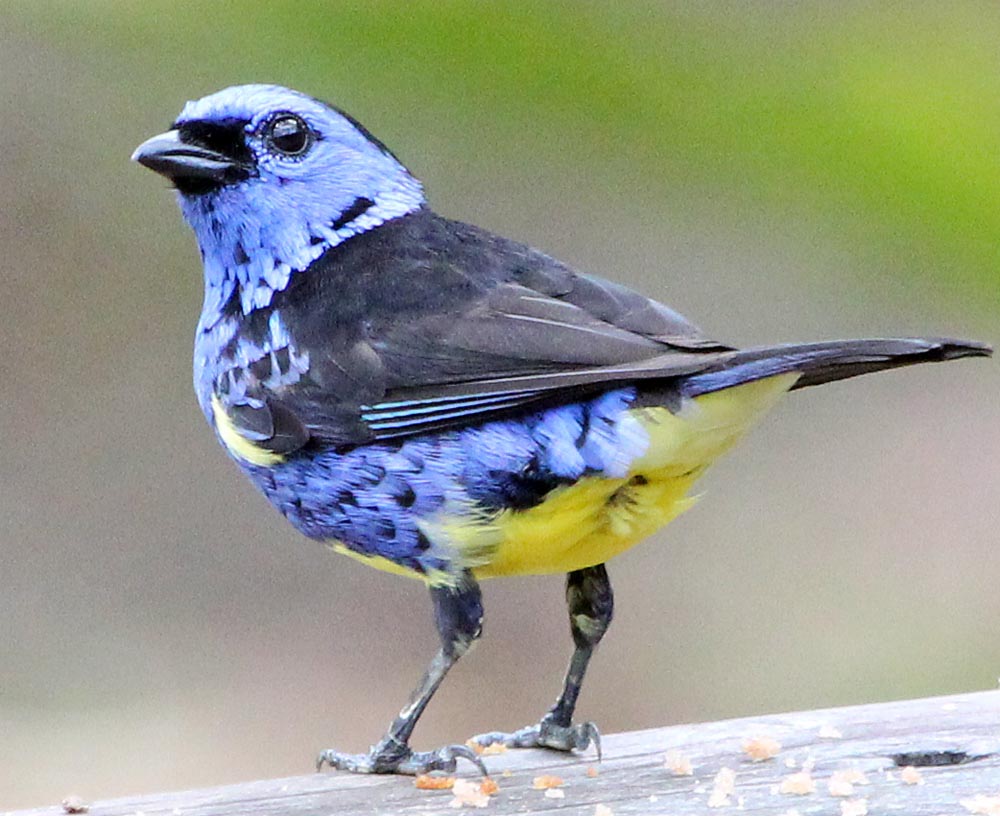 'Torquoise Tanager', (Antonio's Lodge, Brazil).
'Torquoise Tanager', (Antonio's Lodge, Brazil). 'Paradise Tanager', (Canopy Tower, Amazonia Lodge, Peru).
'Paradise Tanager', (Canopy Tower, Amazonia Lodge, Peru).The family Cebidae contains some of the more commonly seen primates such as Capuchins and Squirrel Monkeys.
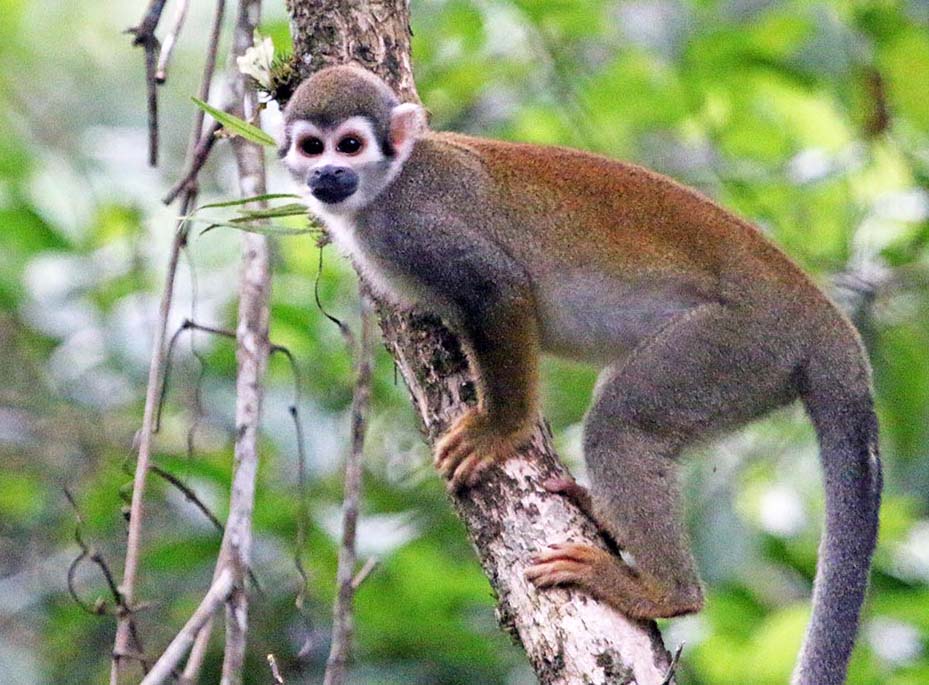 'Humboldt Squirrel Monkey' (Yarina Lodge, Ecuador)
'Humboldt Squirrel Monkey' (Yarina Lodge, Ecuador)The family Pitheciidae includes some of the more unusual looking and lesser known primates, such as Titi, Saki, and Uakari. Recent taxonomic classification studies has revealed there are many species of Titi Monkey, and they are endemic to small areas. They usually have brown, grey or reddish colours. Some species have a different coloured forehead or a unibrow. Unusually for primates, they mate for life. Poor buggers.
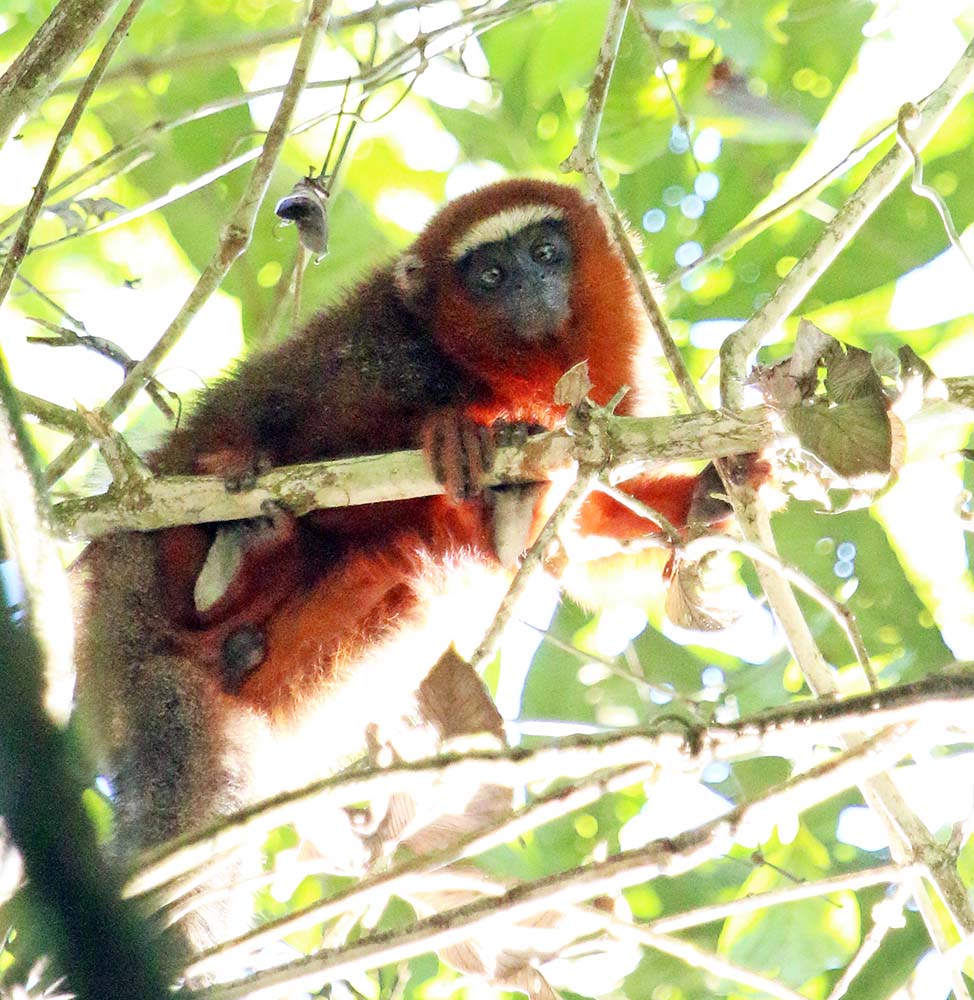 'White-tailed Titi Monkey', (Yarina Lodge, Ecuador)
'White-tailed Titi Monkey', (Yarina Lodge, Ecuador)Big (and small) cats of the family Felidae are the major predators in many of the more pristine rainforest areas, however, they are seldom seen by the casual visitor.
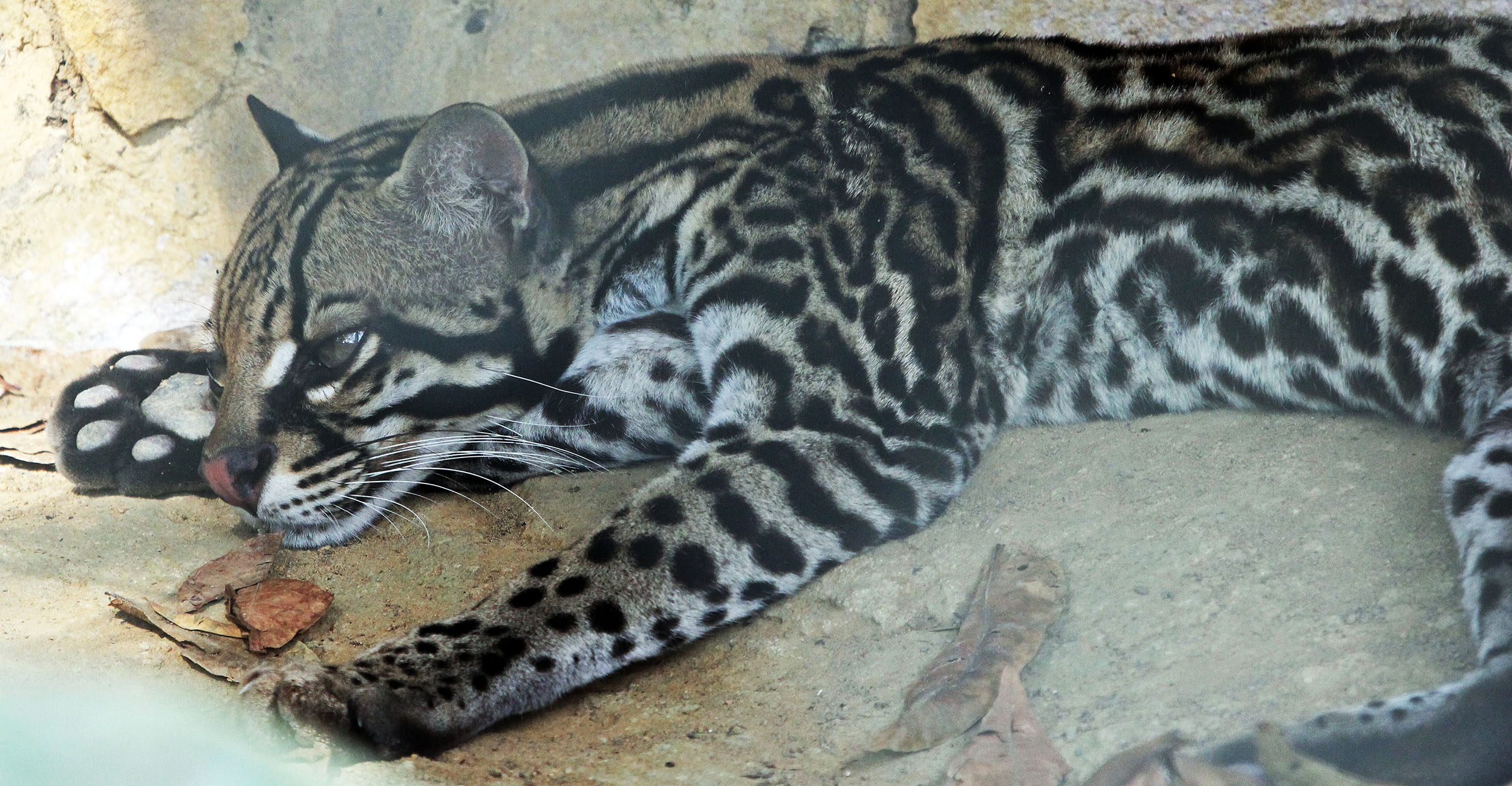 'Ocelot' (in captivity, Manaus Zoo, Brazil).
'Ocelot' (in captivity, Manaus Zoo, Brazil).Places to experience the tropical American rainforest
There are so many great places (and lodges) to explore the lowland rainforest in the tropical Americas. In Peru there is: Amazonia Lodge and the lower parts of Villa Carmen Lodge. In Ecuador: Yarina Lodge in the Amazon. In Colombia: Amacayacu National Park along the Amazon River. And in the biggest country in South America, Brazil, there is: Antonios Jungle Lodge in the Amazon.



